Safety Manual - English

The Culture of Safety
Safety is not simply an understanding. It is not knowledge or even a learned set of policies or standards. Safety is a Culture, it permeates our meetings, planning, and production. Safety is not optional. It is not negotiable. When you joined East Coast Facilities, Inc. as a team member, you joined a company that cares about people, about their well-being, and therefore by extension their SAFETY!“Safety is a Culture”
This culture of safety starts with YOU. It takes individual effort, appreciation, and participation to support an overall culture. Learn from the principles of this safety program. Appreciate how those principles could be applied to any number of matters that may not be specifically covered in this manual. We appreciate your hard work and your dedication to your job with our family. It is our earnest hope, that you will be well prepared for your work assignments by absorbing the training in this safety manual. Thank you in advance for contributing to our Culture of Safety.
Overview of Program
East Coast Facilities, Inc. is a unique company. Our team members can be performing any number of services in a number of regions and climates simultaneously. At the same moment that a crew may be painting the interior of a logistical center in New Jersey, another could be plowing snow in Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, and yet another cutting turf grass in Miami Florida. East Coast self-performs the vast majority of its work, it is imperative that you are specifically trained for your assignments. With this in mind, cross-trained employees, who learn a variety of skills become very valuable assets to the firm; operating as a multi-tool instead of a simple hammer. We want you to become a safely deployed multi-tool, and so you will receive safety training on a variety of services, perhaps including those you may not have yet been given to do.“We want you to become a safely deployed multi-tool”
Our safety program is a blended approach that includes written instructions, on-the-job field training, weekly safety meetings, and from time to time classroom education. This manual will include a variety of topics related to safety standards and rules we employ at East Coast Facilities, Inc. Other safety and job-specific training will be made available from time to time. As an individual it is important to remember, that safety starts with you. You play a vital role in the safe working conditions of our organization.
“We must never forget that the highest appreciation is not to utter words, but to live by them." – Former U.S. President John F. Kennedy
SAFETY COMMITTEE
East Coast Facilities, Inc. has established a safety committee that represents the collective service centers of the company. The members of the committee are made up of both Executive and Operations Management leaders, and at times Field Representatives; usually Team or Crew Leaders. The charter of the Safety Committee is to do the following:- Promote our Culture of Safety
- Take the lead in training and safety initiatives
- Hold planning meetings
- Create safety training schedules and components
- Identify and address unsafe environments and or practices within our company
Current Members
Edwin Torres - Committee ChairmanConnor Peery - Co-Chair
Jonathan Villafañe - Member
Daniel Chavez - Member
Rigoberto Hernandez - Member
Fernando Cruz - Member
Jose Fernandez - Member
Instructions
The Chairman should moderate the meeting, being careful to allow all Members to contribute to the meeting. Long before the meeting is scheduled, the Chairman should request agenda items from each member of the Committee. The Chairman should designate one Member to record minutes. The minutes will be approved by the Chairman and then circulated for posting to each Service Center and Satellite location of the Company. The meeting should not last more than 2 hours. (Inter-quarter conference calls should not last more than 30 minutes) The Co-Chair should be able to stand in for the Chairman if the Chairman is not available. The Chairman may approve others to attend the meeting, including other managers, crew leaders, crew members, or outside consultants.“The safety of the people shall be the highest law." – Marcus Tullius Cicero, Roman philosopher born in 106 BC
PHYSICAL FITNESS & HEALTH
Reducing Musculoskeletal Injuries (MSI) On the Job Employers and employees share responsibility for health and safety in the workplace. An MSI can be defined as an injury to a person of the muscles, tendons, ligaments, joints, nerves, blood vessels, or related soft tissue that is caused or aggravated by work; this includes overexertion injuries and overuse injuries.Trades workers are “industrial athletes” that require fitness training, biomechanical skill training, and education on how to reduce the risk of MSI’s. Just like a worker’s tools are engineered to optimize efficiency, a worker’s body must also have the proper mechanics to perform at peak levels; striving to be the “industrial athlete”.
“Trades workers are industrial athletes”
Performing even simple tasks incorrectly places unnecessary stresses on the muscles and spine that build up over time, wearing the body down. Given that most people find it quite normal or acceptable to warm up before a gym session or to play sports, it makes equally good sense for workers to prepare their bodies before facing the physical demands of manual labor.
Achieving good physical conditioning reduces the risk of a workplace MSI and supports the overall health or wellness of the employee.
As an example, industry-specific workplace stretching programs are intended to reduce the chance of strain or sprain injury through increased flexibility, improved range of motion, improved posture, and stress relief.

But what other ways can you build your body and become an industrial athlete? On the next page, you will see a few things that you should keep in mind. Remember that your job is a physically demanding job. And being an industrial athlete is a winning formula.
How to Become an Industrial Athlete
#1 Eat Healthy

#2 Get Exercise

#3 Get Rest
#4 Drink Lots of Water
DRUG & ALCOHOL-FREE WORKPLACE POLICY
The use, sale, or personal possession (i.e., on the person, in a toolbox, desk, locker, at any of our facilities, job sites, or vehicles) of illegal drugs while employed by East Coast Facilities at any time, is a dischargeable offense and may result in criminal prosecution. Any illegal drugs found on or within company property, or on job sites will be turned over to the appropriate law enforcement agency.

The following illicit "drugs" are those that East Coast Facilities will conduct testing for; Marijuana/Cannabis (THC); Cocaine (COC); Opiates (OPI); Amphetamines (AMP); Phencyclidine (PCP) using a 5-panel drug testing kit.
Note, that for prospective or current employees with residence in one of the following jurisdictions, Marijuana/Cannabis (THC) is exempt as an illicit drug for purposes of testing and employment eligibility at East Coast Facilities due to changing laws. The chart below lists the laws currently in place that impact the disposition of the local workforce. All aforementioned requirements regarding use, sale or personal possession at work remain in full force.
| Jurisdiction | Is Recreational Use Legal? | Year Legalized | Is Medical Use Legal? | Year Legalized |
| Illinois | Yes | 2019 | Yes | 2013 |
| Florida | No | Yes | 2016 | |
| Georgia | No | Yes | 2015 | |
| Maryland | No | Yes | 2013 | |
| Pennsylvania | No | Yes | 2016 | |
| New Jersey | Yes | 2020 | Yes | 2010 |
| Virginia | Yes | 2021 | Yes | 2020 |
Employees taking prescription or non-prescription medications that may affect their ability to work must report this use to “Human Resources”, since the use of such drugs may impair the employee’s ability to perform assigned duties. This must be reported in writing by sending an email to HR@ecf.email This reporting requirement is intended to protect the safety of each employee, co-workers, and the public. Employees failing to follow this instruction can be subject to disciplinary action.
Symptoms of impairment include dizziness, drowsiness, headache, nausea, blurred vision, slowed reactions, inability to focus, being easily confused, slurred speech, and feeling manic or overconfident.
Medicines with the potential to impair driving ability or the operation of mechanical tools and equipment include some pain relievers, anxiolytics, antidepressants, sleeping aids, antiepileptics, sedating antihistamines, antipsychotics, medicines used in the eyes, cough and cold medicines, and some heart medicines.
ALCOHOL USE OR POSSESSION ON THE JOB
The use or personal possession (i.e., on the person, in a toolbox, desk, locker, or vehicle) of alcohol during work time, including rest and meal periods or on Company property at any time, is a dischargeable offense.Notwithstanding this, there may be occasions, removed from the usual work setting, at which it is permissible to consume alcohol in moderation, with management approval. Employees who consume alcohol under such circumstances shall not report back to work without the General Manager’s approval during that workday.
OFF THE JOB SELLING, MANUFACTURING, OR DISTRIBUTING OF ILLEGAL DRUGS
Employees who have been arrested for the manufacture, sale, or distribution of illegal drugs will be placed on a “leave of absence” while awaiting the results of their arrest. Employees convicted of distributing, selling, or manufacturing illegal drugs (or similar charges) will be terminated.PREVENTATIVE MEASURES
To protect all employees and the Company, the Company will take reasonable measures to find out if alcohol or illegal drugs are located or being used on company property. These measures include, but are not limited to, the following:- Educating all employees on the company’s “Drug-Free Workplace Policy”.
- Compliance with all applicable requirements or government agencies (such as the Department of Transportation) concerning substance abuse. This includes drug and alcohol testing for safety-sensitive positions.
- Training all supervisors on substance abuse issues, including “confidentiality” and “reasonable suspicion.”
- Searches of company property by authorized personnel. Law enforcement authorities may be contacted to assist in such actions.
- Searches of personal property located on company premises. The supervisor will conduct such searches after consultation with the company’s representative due to reasonable suspicion. Any search conducted will be witnessed and documented. These searches will not be conducted if the person refuses to submit to such a search. Upon refusal to submit to such a search, the purpose of the search and the potential ramifications of refusal will be carefully explained to the employee. Continued refusal to submit to such a search will result in the employee’s immediate removal from duty and may result in discharge for insubordination.
Drug and alcohol testing will be conducted when an employee is involved in an on-duty accident (i.e., personal injury, property damage, product damage, equipment damage) and/or when a consensus of supervisors and/or management personnel has reasonable suspicion of drug or alcohol use.
Testing will also be conducted if an employee’s supervisor has determined that the employee is not fit for duty and has a reasonable suspicion that alcohol or illegal drug use may be involved. Before proceeding further, the supervisor must confirm his/her suspicion with another supervisor or management personnel. The supervisors should meet privately with the employee and conduct their discussions in a “confidential” manner.
DRUG TESTING PROCEDURES
Reasonable Suspicion Drug TestingAn employee who is asked to take an alcohol or drug test based on reasonable suspicion, whether involving an accident (i.e., personal injury, property damage, product damage, equipment damage) or not, will be placed on “administrative leave” for three (3) days, or until the results of the tests are known. An employee who refuses to take the test will be counseled as to the purpose of the test and the consequences of refusing to take the test. Continued refusal to take the test will result in the employee’s immediate removal from duty and discharge for insubordination.
- If the test results indicate no use of illegal drugs or alcohol, the employee will be returned to duty with back pay if applicable.
- If the Medical Review Officer’s findings indicate reportable levels of illegal drugs or alcohol the employee’s administrative leave will be changed to a termination.
- Employees who are terminated due to illicit drug use are encouraged to seek professional treatment. The terminated employee can call 1-800-662-HELP or go to drugabuse.gov for further assistance.
- If the terminated employee wishes to be considered for re-hire; he/she is required to obtain drug or alcohol addiction treatment. They will be required to demonstrate that they have undergone treatment. They may reapply no less than 30-days from the date of their termination. Re-application does not guarantee an offer of employment will be extended.
- On rare occasions, executive management may elect to provide back pay to employees who underwent drug addiction treatment. This discretionary action gives consideration to team members with a record of excellence demonstrated over many years of service.
“Employees who are terminated due to illicit drug use are encouraged to seek professional treatment. The terminated employee can call 1-800-662-HELP or go to drugabuse.gov for further assistance.”
Department of Transportation (DOT) Drug Testing
All truck drivers with CDL licenses will be subject to drug and alcohol testing on a random basis in accordance with the “Department of Transportation Regulations”
HANDBOOK - PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
You are required to utilize Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for various job assignments. You will be provided with each piece of PPE that is applicable to your job assignments. Lost or negligently damaged PPE items are your responsibility. Worn PPE can be replaced, by asking your supervisor for new equipment.Examples of PPE
- Safety Glasses, Goggles – Eye Protection
- Safety Vests or Safety Shirts- Visibility
- Gloves (Nitrile, Kevlar, and Leather)- Hand Protection
- Face Shields- Eye & Face Protection
- Hard Hats- Head Protection
- Chaps – Protect Legs
- Respirators- Protect the Lungs
- Safety Boots- Protect Feet & Ankles
- Safety Harnesses – Aerial Work Fall Protection
PPE APPLICATIONS CHART
| Equipment / Task | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| General Policing | X | X | X | |||||
| General Labor | X | X | X | |||||
| Back Blower | X | X | X | |||||
| Line Trimmer | X | X | X | |||||
| Stick Edger | X | X | X | |||||
| Lawn Mower | X | X | X | |||||
| Pole Saw | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| Chain Saw | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| Hedge Trimmer | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| Chemical Mixing | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| BackPack Spraying | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| Inside Warehouse Facilities & Yard Areas | X | X | X | |||||
| Paint Spraying | X | X | X | X | ||||
| Operating Seal Coating Equipment | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| Replacement of Light Bulbs | X | X | X | |||||
| Operating a Pressure Washer | X | X | X | |||||
| Working around a Loader, Back Hoe, Skid Steer | X | X | X | X | ||||
| Operating a Wood Chipper | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| Operating an Aerial Lift | X | X | X | X | ||||
| Operating Concrete Mixer | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| Operating Hand Drills, Saws, Similar Power Tools | X | X | X |
HANDBOOK - SAFE DRIVER STANDARDS
The driver of company-owned fleet is responsible for the safety of his/her fellow team members and the public at large. The safe operation of any vehicle requires skill and focus. It should be your goal, to become a qualified SAFE driver.
- Always observe the speed limit and maintain as steady a speed as possible.
- Do not accelerate the vehicle in an abusive manner. Gently accelerate.
- Keep the windows closed at highway speeds.
- When climbing a hill, accelerate gently before beginning, maintain a steady throttle until near the top then ease off on the gas.
- Turn off the engine when parking for more than a minute; never leave the vehicle with the engine running.
- When coming to a stop, allow the rolling resistance and wind to help slow you down.
- When merging lanes with other traffic, time your approach with other vehicles to do so smoothly. Utilize team members if possible to confirm you have a clear passage.
- Avoid braking in turns; break before going into a turn.
- Avoid revving a cold engine or one that is about to be shut off.
- Drive manual transmissions in the highest possible gear without lugging the engine.
- Anticipate stops as far ahead as possible, especially when pulling a trailer.
- Hold the steering wheel as steady as possible. Use two hands whenever possible.
- Distribute weight loads as evenly as possible on both the truck and trailer unit if applicable.
- Come to a complete stop before backing up.
- Plan your responses to traffic as early as possible and be patient.
- Always check your oil, fuel, lights, horn, brakes, and mirrors before starting out.
- Check mirrors frequently. Be aware of your surroundings.
- Always use a spotter when backing up.
HANDBOOK- PROPER LIFTING
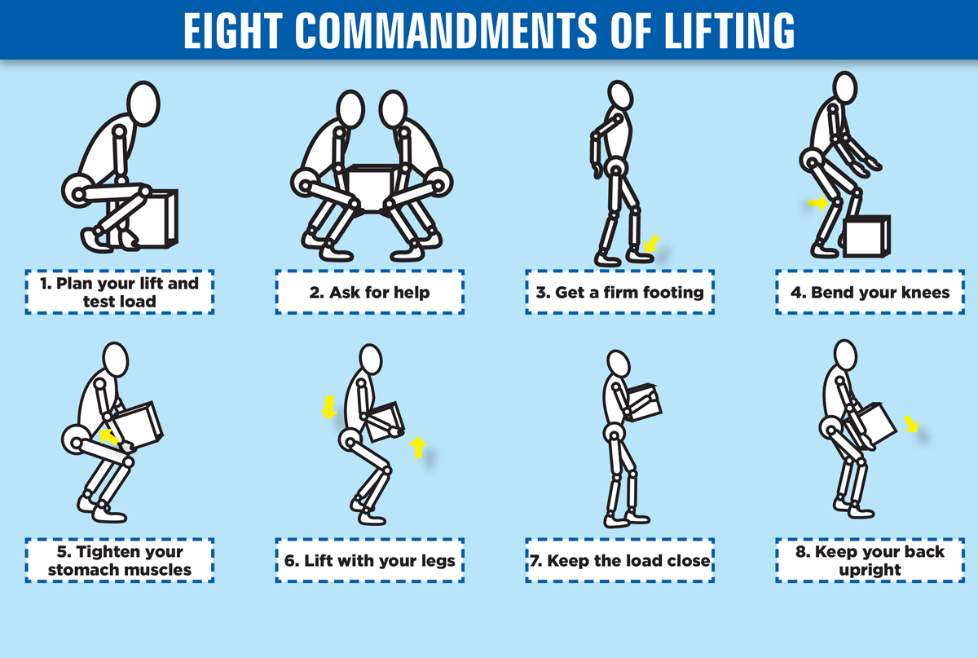
Lifting heavy items is one of the leading causes of injury in the workplace. In 2001, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that over 36 percent of injuries involving missed workdays were the result of shoulder and back injuries. Overexertion and cumulative trauma were the biggest factors in these injuries. When employees use smart lifting practices and work in their "power zone," they are less likely to suffer from back sprains, muscle pulls, wrist injuries, elbow injuries, spinal injuries, and other injuries caused by lifting heavy objects.
Follow these tips to avoid compressing the spinal discs or straining your lower back when you are lifting:
- Keep a wide base of support. Your feet should be shoulder-width apart, with one foot slightly ahead of the other (karate stance).
- Squat down, bending at the hips and knees only. If needed, put one knee to the floor and your other knee in front of you, bent at a right angle (half kneeling).
- Keep good posture. Look straight ahead, and keep your back straight, your chest out, and your shoulders back. This helps keep your upper back straight while having a slight arch in your lower back.
- Slowly lift by straightening your hips and knees (not your back). Keep your back straight, and don't twist as you lift.
- Hold the load as close to your body as possible, at the level of your belly button.
- Use your feet to change direction, taking small steps.
- Lead with your hips as you change direction. Keep your shoulders in line with your hips as you move.
- Set down your load carefully, squatting with the knees and hips only.
- Keep in mind:
- Do not attempt to lift by bending forward. Bend your hips and knees to squat down to your load, keep it close to your body, and straighten your legs to lift.
- Never lift a heavy object above shoulder level.
- Avoid turning or twisting your body while lifting or holding a heavy object.
HANDBOOK – USING STEP LADDERS
Step ladders are very often both a central part of a paint job, but also a key danger area. Here are some tips on how to minimize the likelihood of a ladder-related accident:Inspect the ladder:
- Take time to check the condition of the ladder both before and after use.
- Check that the ladder is sufficiently robust to support your weight.
- Make sure the steps are free of oil, wet paint, mud, or any other potentially slippery substance.
- Clear the area around the ladder from any clutter. Make sure that no electrical cords or wire leads are close.
- If the ladder needs to be in front of a door, consider locking the door to prevent surprise openings.
- If the ladder is in a high-traffic area, draw attention to this fact in the house – a hand-written sign would do.
- Make sure the floor is even and stable. Avoid wet or slippery surfaces.
- Always support the ladder at four points.
- Wear Suitable shoes/boots only.
- Never climb onto wet or slippery steps, make sure they are dry.
- Never overstretch – do not climb beyond the last three steps of a ladder.
- Keep your shoulders between the rails and don’t over-reach – move the ladder instead.
- Always keep 3-point contact with the ladder.
- If your ceiling is high, but your ladder too small, don’t try to overreach yourself – renting or borrowing a suitable ladder is much safer.
- Don’t let your children climb up the ladder: prevent access at the end of the day if you have to, or fold it up after use.
- Be prepared for an unforeseen vertigo attach – don’t look down, breath slowly and steadily, and go back down step by step.
POLICY ON HYDRATION
Hydration is not a recommendation; it is a requirement.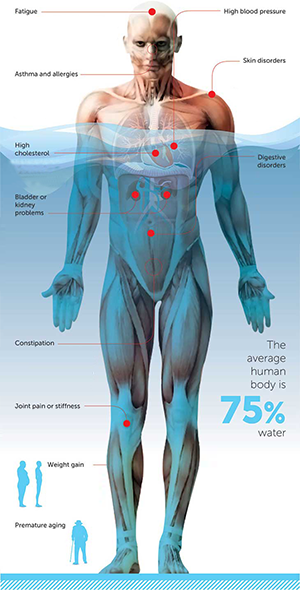
YOU ARE RESPONSIBLE TO BRING ADEQUATE WATER WITH YOU TO WORK EVERY DAY.
What does dehydration cause?
1. Fatigue
Dehydration causes the enzyme activity in the body to slow down which can result in feeling tired and fatigued.
2. High blood pressure
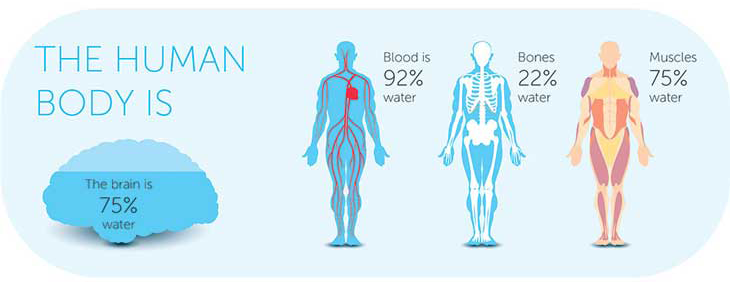
When fully hydrated the blood sits at around 92% water. When dehydrated blood becomes thicker causing resistance to blood flow and therefore elevated blood pressure.
3. Asthma
When dehydrated your body will restrict airways as a means to conserve water.
4. Skin disorders
Dehydration affect the elimination of toxins through the skin leading to all types of disorders, including dermatitis, psoriasis, wrinkling and discoloration.
5. High cholesterol
The body produces more cholesterol when dehydrated in order to prevent water loss from cells.
6. Digestive disorders
A shortage of water that contains valuable alkaline minerals can lead to digestive disorders including ulcers, gastritis and acid reflux.
7. Bladder or Kidney infections
When the body is dehydrated you accumulate more toxins and waste in the bladder and kidneys, an environment where bacteria thrive resulting in infection, inflammation, and pain.
8. Constipation
The colon is one of the primary regions the body draws water from. Without adequate water, waste moves through much more slowly or sometimes not at all.
9. Joint Pain
All joints have fluid which is composed mainly of water. When the body is dehydrated cartilage is weakened and joint repair is slow resulting in pain and discomfort.
10. Weight Gain
When dehydrated the cells are depleted of energy and as a result, people tend to eat more when, in reality, the body is thirsty.
11. Premature aging
When dehydrated for a long period of time the body’s largest organ, the skin, begins to wrinkle and wither prematurely.
How much water should I drink per day?
The amount of fluid you need depends on factors like your sex, level of physical activity, and the climate where you live. The hotter the climate, the more you need to drink. If you are working in a hot environment, keep these tips in mind:
- Drink at least 1 pint (2 cups) per hour to stay hydrated.
- Cool fluids like water or a sports drink are good choices.
- Avoid sugary (i.e., regular soda, sweetened tea, etc.), and alcoholic beverages. These beverages will cause you to urinate more, which can make you more dehydrated.
Monitor the color of your urine. One sign of dehydration is dark-colored urine, ranging from dark yellow to orange or even darker. If you start drinking enough water, your urine should change to pale yellow. Drink plenty of water or other appropriate fluids often. By the time you feel thirsty, you are already dehydrated.
Definitions of Heat-Related Illnesses and what to do if they occur
If your body is unable to cool off by sweating, you can develop a heat-related illness. Heat-related illnesses are very serious and can even lead to death. Heat-related illnesses include heat exhaustion and heatstroke. The quicker you can recognize and treat these conditions, the better. Descriptions of each of these heat-related conditions and tips for treating them are presented below.
Heat exhaustion occurs when dehydration has not been corrected, and your body becomes overheated. Signs and symptoms of heat exhaustion include heavy sweating, dizziness, nausea or vomiting, headache, or pale skin.
What to do
- Move to a cooler place or seek shade.
- Drink small amounts of cool water or a sports drink.
- Remove or loosen outer or heavy clothing.
- Seek medical attention if conditions do not improve.
What to do
- Get medical assistance or call 911.
- Cool the victim immediately using cold packs, an ice bath, or a water hose.
- Try fanning the victim as another way to help lower their body temperature.
- Move the victim to a shady, cool place.
- Monitor body temperature.
- Remove unnecessary clothes.
- Do not give the victim anything to drink if they seem confused or disoriented. If you are unsure of the victim's mental alertness, ask them to tell you where they are, their name (if you know them or can find their identification papers), and the day of the week. If they cannot answer these questions correctly, it is likely that they are disoriented.
LANDSCAPE MAINTENANCE – SAFETY RULES
- No smoking on job sites.
- Use of alcohol or use of narcotics during the working day or working under the influence of alcohol or narcotics is prohibited.
- Mower operation - turn off the engine when it is necessary to touch any part of the mower, except the handle or when removing the catcher.
- When using edgers, weed-eaters, or grinders you must wear eye protectors, safety glasses, or shields, and with chainsaws, ear protection must also be worn.
- Engine - running adjustments will be made only by authorized employees who have received adjustment instruction.
- When removing or sharpening blades, disconnect the wire from the spark plug and wear gloves.
- When using blowers wear eye & ear protectors.
- When mixing or spraying herbicides or pesticides read and follow label instructions and wear rubber gloves.
- When traveling to and from job sites, no one rides in the bed of a truck.
- To protect your feet, wear work boots that cover the ankle completely. No Tennis Shoes or Sandals! No Boots - No Work!
- Report all accidents to your supervisor or to the office immediately whether or not medical attention is required.
- While using a pole pounder or stake driver, a hard hat must be worn.
- No employee is to store or transfer any material from or into an unmarked or unlabeled container or package. If you discover an unmarked or unlabeled container or package, report it to your supervisor immediately.
IRRIGATION MAINTENANCE – SAFETY RULES
- No smoking on job sites.
- Always disconnect power to controllers before working on them.
- Observe OSHA standards for trenching and shoring.
- Wear safety glasses when unclogging nozzles with water running, soldering, operating equipment, gluing, or cutting pipes.
- Always shut the water off before disassembling valves.
- Observe all manufacturer's safety rules when operating equipment (trenchers, tamping equipment, etc.).
- Wear gloves when cutting pipes.
- Always locate underground utilities before excavating to identify potential hazards.
- Use safety cones and barricades during excavation.
- Secure/cover all temporary excavation.
- Use of alcohol or narcotics during the working day or working under the influence of alcohol or narcotics is prohibited.
- Report all accidents to your supervisor or to the office immediately, whether or not medical attention is required.
TREE TRIMMING – SAFETY RULES
- No smoking on job sites.
- Use of alcohol or use of narcotics during the working day or working under the influence of alcohol or narcotics is prohibited.
- Ensure the area is marked and that there are no people in the immediate area. Other workers should be twice as far as the height of the trees being felled.
- Identify electrical lines in and near the work area.
- Chipper operation - turn off the engine when it is necessary to clear a blockage or clog.
- Only use the equipment in harmony with the manufacturer's safety labels and recommendations; a manual is with the machine and accessible for review.
- Never place your body or any part of it within the brush guards near the debris intake cogs/wheels
- When using clippers, blowers, and chain saws you must wear eye protectors, safety glasses, or shields, and with chainsaws ear protection must also be worn. Hard Hats are a requirement.
- Chainsaws
- Before Operation
- Check controls, chain tension and all bolts and handles to ensure they are functioning properly and adjusted according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Ensure the chainsaw engine is the appropriate size for the project.
- Check that all safety devices are working properly.
- Do not operate a chainsaw that is damaged or has disengaged safety devices.
- Look for nails, spikes, or other metal objects prior to cutting.
- Clear away dirt, debris, small tree limbs, and rocks from the chainsaw’s path.
- Never work alone.
- While Operating
- Start the saw on the ground or another firm support with the brake engaged.
- Keep both hands on the handles and maintain secure footing.
- Plan where the object will fall; ensure that the fall area is free of hazards; and avoid felling an object into other objects.
- Plan the cut; watch for objects under tension; use extreme care to bring objects safely to the ground.
- Be prepared for kickback; avoid cutting in the kickback zone and use saws that reduce kickback danger (chain brakes, low kickback chains, guide bars, etc.).
- Do not cut directly overhead.
- Shut off or release the throttle before retreating.
- Take breaks as needed, as fatigue increases the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Before Operation
- Engine - running adjustments will be made only by authorized employees who have received adjustment instruction.
- When removing or sharpening blades, disconnect the wire from the spark plug and wear gloves to remove cutting teeth.
- All harnessing and safety standards shall be utilized when operating bucket trucks.
- Bucket Operators shall be very careful around traffic, parked vehicles, buildings, and other obstacles.
- Employees are required to tie off to the bucket when performing this work and make sure the wheels are chocked.
- Spotters must be used when operating bucket trucks to control traffic and warn of obstacles
- When traveling to and from job sites, no one rides in the bed of a truck.
- To protect your feet, wear work boots that cover the ankle completely. Boots must steal toe.
- Report all accidents to your supervisor or to the office immediately whether or not medical attention is required.
SNOW REMOVAL – SAFETY RULES
- No smoking on job sites.
- Use of alcohol or use of narcotics during the working day or working under the influence of alcohol or narcotics is prohibited.
- Heavy Equipment is only to be operated by authorized personnel, who have clearly demonstrated that they can safely operate heavy equipment for the purposes of snow removal.
- Plow Trucks / Salters are only to be operated by authorized personnel, who have clearly demonstrated that they can safely operate plow trucks/salters for the purposes of snow removal.
- Snow Blowers are only to be operated by authorized personnel, who have clearly demonstrated that they can safely operate snow blowers for the purposes of snow removal.
- No repairs should be made to the equipment without the expressed authorization of the Operations Manager.
- When cleaning clogged snow from a snowblower, turn off the motor, disconnect the wire from the spark plug and wear gloves.
- Fueling equipment should only be done by trained personnel, who understand the correct fueling procedure.
- All personnel must dress warm, with multiple layers, including thermals, hats, gloves, and waterproof insulated work boots.
- Report all accidents to your supervisor or to the office immediately whether or not medical attention is required.
PAINTING OPERATIONS – SAFETY RULES
Using Protective Equipment

The basic gear you need for a safe paint job are:
- Gloves
- Safety Glasses or goggles
- Dust mask
- Safety Boots
- Wear the appropriate gloves: cloth or leather gloves for sanding and scraping, impermeable gloves for applying water-based paint, solvent-resistance chemical gloves for handling solvent-based products.
- Use eye goggles or glasses, or a face mask.
- Lung protection:
- Wear an anti-dust mask whilst sanding a surface or a solvent-respirator if working with solvent-based products.
- Ensure good ventilation with open windows and doors.
- Remove sources of ignition.
All organic-based solvents – including white spirit, solvent-based paints, solvent-based thinners and primers, solvent- based wood treatment products as well as paint strippers – represent potential health hazards, and require that particular precaution be taken both in use and in storage.
Rules Specific to Solvent-based Products:
- Read the label carefully for information on safety and health-related issues.
- Solvents are highly flammable – keep these paints away from all sources of heat, and never expose directly to an open flame.
- Store in cool, well-ventilated areas.
- Keep these products out of reach of pets and children.
- Dispose of rags properly – rags soaked with oil-based material can ignite spontaneously if not spread out to dry.
- Ensure good ventilation with open windows and doors.
- Wear protective equipment.
- Keep children and pets out of the painted area.
- Water-based paints; a viable alternative to solvent-based paint:
- To a large extent, water-based paints pose fewer risks and health hazards than solvent phase paints. Modern, high-quality water-based paint offers an excellent performance profile – superior durability and color retention, excellent washability, for example. They are also more convenient to use – low in odor, they dry quickly, and brushes can be cleaned with warm, soapy water, with no need for white spirit or turpentine. And of course, they are more environmentally friendly.

Safety Rules - General
- No smoking on job sites.
- Use of alcohol or use of narcotics during the working day or working under the influence of alcohol or narcotics is prohibited.
- Always take note of any cautions or potential dangers indicated on the paint can, and take the appropriate preventative action.
- Always remember to use protective equipment, especially eye goggles and a face mask to cover the mouth and nose.
- Take precautions when handling and storing solvents.
- Wash your hands after use.
- Remember to ensure adequate ventilation in rooms you are painting – Open windows and doors wherever possible.
- Avoid exposure to solvents as much as you can.
- Never smoke when handling solvents.
- Solvents are highly flammable – Never expose solvents to an open flame.
- Keep children away from areas you are painting.
- Water-based paints are more environmentally friendly than solvent-based alternatives, and so wherever possible should be given serious consideration.
- Always take care to follow the precautions indicated on the product.
- Try to buy exactly as much paint as your job requires – so disposal is not an issue.
- If you do have some paint left, try to find some use for it – Maybe apply another coat.
- To store paint for the future, make sure the lid is on tightly – this prevents air and dirt from getting in, and helps the paint last longer.
- Contact your local authority for guidance on the safe disposal of paint – Many have schemes for this purpose.
- If you have to clean tools with a solvent, try to re-use the solvent as many times as possible for cleaning.
- Never pour leftover paint down the drain.
- Never put leftover liquid paint in with your other waste.
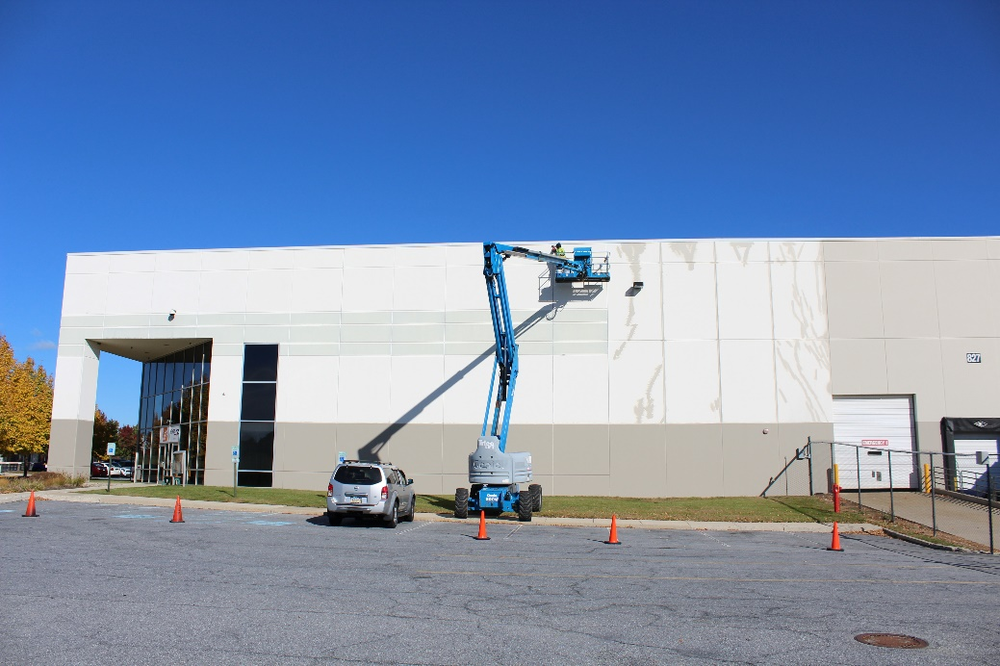

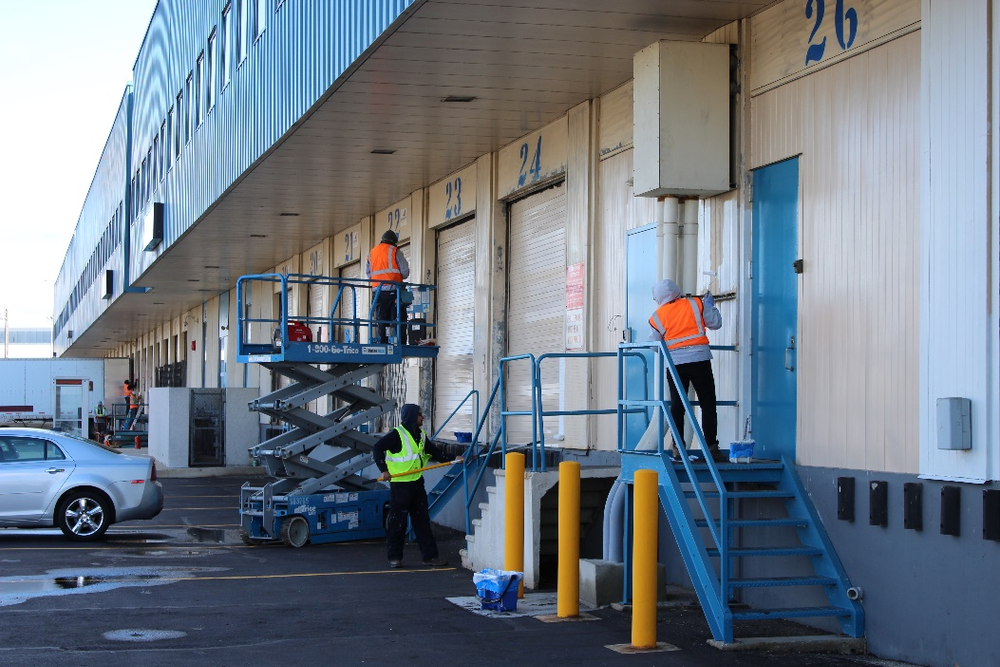
- No person may operate an aerial lift without certification by the company certified trainer
- No person may operate a lift alone, without a ground spotter
- Areas must be properly coned off to protect the team, pedestrians, and traffic
- Controlled Access Zones:
A controlled access zone is a work area designated and clearly marked in which certain types of work may take place without the use of conventional fall protection systems – guardrail, personal arrest, or safety net. Controlled access zones are used to keep out workers other than those authorized to enter work areas from which guardrails have been removed. Controlled access zones must be defined by a control line or by any other means that restrict access. Control lines shall consist of ropes, wires, tapes, or equivalent materials, and supporting stanchions.
- Controlled Access Zones:
- You must wear fall protection
- Activities where fall protection is needed include:
- Ramps, runways and other walkways
- Excavations
- Hoist areas
- Holes
- Roofing work
- Wall openings
- Hazard of falling into dangerous equipment
- Activities where fall protection is needed include:
- You must be “hooked in” before you even turn on the lift
- You must wear a hard hat and safety vest or safety shirt
- Specific Lift Training and Certification is conducted outside of this manual, as it is extensive and issued as a specific job assignment.
SEAL COATING OPERATIONS – SAFETY RULES
East Coast Facilities utilizes water‐based asphaltic products and acrylic products that are environmentally and user‐friendly. Our vendor of choice is the SealMaster® company. SealMaster® has locations up and down the east coast that support our services centers and their respective operations. Project Managers are not authorized to purchase products from another vendor without explicit written authorization from the Vice President of Operations.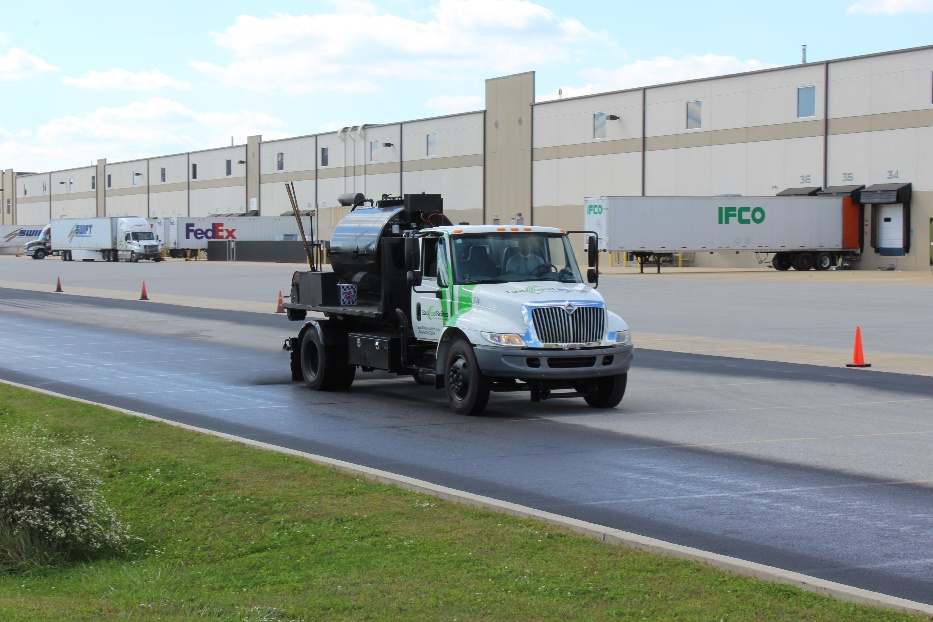 Using Protective
Using Protective Equipment
- The basic gear you need for a safe job site is:
- Gloves
- Safety Glasses or goggles
- Dust mask or a Respirator* (*if you are sensitive to dust or product)
- Safety Boots
- Safety Vest or Safety Shirt
- Wear the appropriate impermeable gloves for applying seal coating products.
- Use eye goggles or glasses, or a face mask.
- Wear an anti-dust mask or a respirator if you have sensitivity to dust or product.
- Handling Seal Coating Products
Accidental spillage of the product must be immediately collected in 5-gallon pales. Each team must have a spill kit for emergency clean-up. If a spill of great scope (95 gallons) occurs, diking must be established, and the onsite crew leader must contact operations to send a tanker to collect the material. If the spill impacts lawn or other porous areas, operations must follow the Hazcom Plan and arrange for appropriate remediation. With this in mind, staging should never be over a porous area. It must always be over and if possible in the middle of a paved area.
 ññññ
ññññ Application Environment
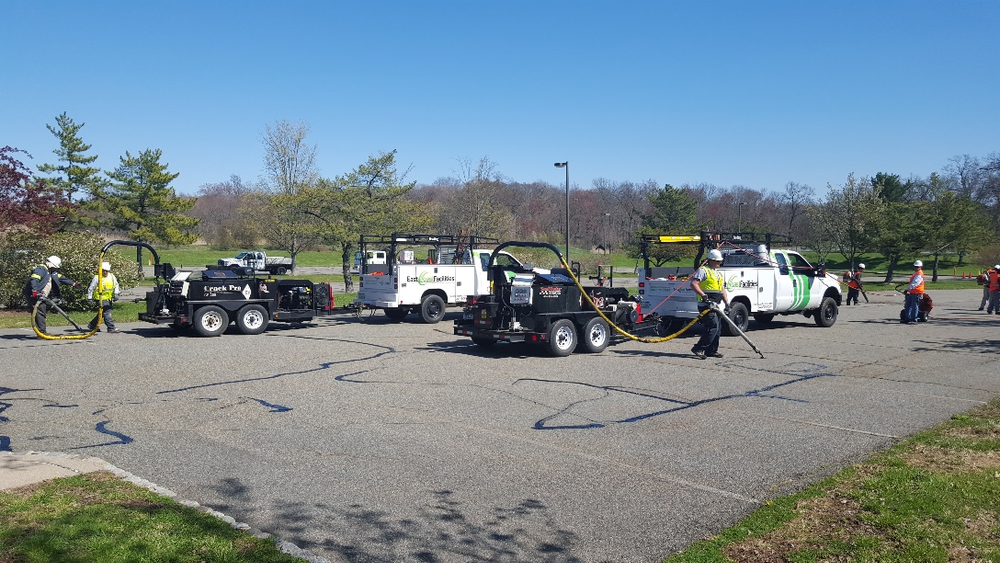

Threats to safety once onsite and performing seal coating, include heat, traffic movements, movement of equipment, lifting, and more.
Safety Rules
- Stay hydrated
- Cone off work areas and limit traffic
- The Crew Leader / Team Leader must assign a flagman
- Observe and use all equipment safety functions, do not disable any safety features of the equipment you are using
- Never back up a seal coating truck or trailer without a spotter
- Where all appropriate PPE
- Watch each other, never take your eyes off your team
- Rotate difficult parts of the job, like spraying, shielding, moving crack sealing boxes
ACCIDENT & INJURY REPORTING
Accidents and injuries must be immediately reported to your supervisor. NO EXCEPTIONS. Failure to immediately report any accident or injury will result in suspension without pay pending review by the safety committee.It is critical to report accidents and injuries, to avoid escalation. Untreated injuries can prove to be far more detrimental to the victim if they go untreated.
You’re the Service Center Manager or designee, will fill out the company’s Accident / Incident Investigation Summary, the same day this Accident or Injury occurs and forward same to HR at hr@ecf.email

FIRST AID
First Aid Training will occur at each Service Center Level; the components of First Aid training are not included in this safety manual; however, it should be noted that the following applies to First Aid:
- Only qualified persons should render first aid
- If a company or external certified person is present when an injury occurs, they should take the lead in rendering First Aid
- If the injury is life-threatening call 911 immediately
- All personnel are trained over the course of their employment in First Responder Training
- All company smartphones issued to company personnel are outfitted with the Red Cross – First Aid Application

OVERVIEW OF SAFETY TOPICS FOR TRAINERS & SUPERVISORS
| Introduction to Safety in Landscaping and Horticultural Services | Protecting Against Noise |
| Arc Welding Safety | Protecting Hands and Fingers |
| Battery Safety | Protecting the Head |
| Bee, Wasp, Hornet, and Yellow Jacket Stings | Protective Gloves |
| Bucket Trucks and Aerial Lifts | Reading Pesticide Labels |
| Caught In or Between Objects | Repetitive Motion |
| Chain Saw Safety | Respirator Fit |
| Chemical Skin Irritants | Rollovers and Rollover Protective Structures (ROPS) |
| Chock and Block | Rotary Lawn Brush and Mower Safety |
| Choosing Spray Nozzles | Safe Operation of Portable Circular Power Saws |
| Color Coding | Safe Use of Hand Pallet Trucks and Electric Carts |
| Dust and Mold | Safe Use of Flammable Liquids |
| Electrical Shock | Safe Use of Hand-Held Tools |
| Equipment and Plant Transport | Safe Use of Hydraulic Systems |
| Equipment with Cutter Bars or Blades | Safe Use of Jacks |
| Federal Department of Transportation (DOT) Placarding | Safe Use of the Power-Take-Off |
| First Aid Kit | Safe Use of Tractors and Self-Propelled Equipment |
| First on the Scene | Safely Starting and Stopping a Tractor |
| Forklift Safety | Safety Means Slow-Moving Vehicle |
| Gas Welding | Selecting a Respirator |
| Grounding Electricity | Skin Irritations Caused by Plants |
| Hand Signals for Vehicle Safety | Small Engine Machine Safety |
| Heat Stress | Spider Bites |
| Hypothermia, Frostbite, and Trench Foot | Spraying Paint |
| Laundering Pesticide-Contaminated Clothing | Stress Management |
| Loading Docks and Warehouses | Struck-By Accidents |
| Lockout and Tagout | Substance Abuse and Accidents |
| Material Handling Devices | Sun Exposure |
| Material Safety Data Sheet | Task Lighting |
| Mixing and Spraying Pesticides | Thorn Bushes |
| Mosquito Bites | Tick Bites |
| No Riders on Lawn Equipment | Tractor Loader Safety |
| Non-Vented Heaters | Tractors, Towed Equipment, and Highway Safety |
| Overhead Electrical Hazards | Tree Pruning and Ladder Safety |
| Personal Eye Protection | Tree Pruning, Trimming, and Felling Safety |
| Pesticide Exposure | Trenching and Excavation Safety |
| Poison Ivy, Poison Oak, Poison Sumac | Wood Chippers and Shredders |
| Portable Fire Extinguishers | Workplace Violence |
| Power Lawn Mowers | |
| Power-Take-Off (PTO) Shielding | |
| Personal Protection Equipment (PPE) for Pesticides | |
| Preventing Falls from Trees | |
| Preventing Falls | |
| Preventing Lifting Overexertion Injuries | |
| Preventing Machine Hazards | |
| Proper Use of Ladders | |
| Properly Cleaning and Storing Respirators | |
| Protecting Against Cold |

If you still have a question, we’re here to help. Contact us
